Nut
Nuts
↪ In the context of fittings, a nut is a typically hexagonal-shaped component that is used to tighten and secure a fitting onto a mating threaded component, such as a pipe or tubing. Nuts are often used in conjunction with ferrules in compression fittings to create a leak-tight seal.
Types
↪ Cap Nuts: Cap nuts have a domed cap that covers the exposed end of a bolt or screw, providing a finished appearance and some degree of protection.↪ Slotted Nuts: Slotted nuts feature slots or openings on the top, allowing them to be secured with a cotter pin or split pin for additional security.
↪ T-Nuts: T-nuts have a flange with prongs that dig into the surface of the material, providing a secure anchor point when installed in wood or plastic.
↪ Hex Nuts: Hexagonal nuts are the most common type, featuring six flat sides and an internally threaded hole. They are tightened using a wrench or socket.
↪ Acorn Nuts: Similar to cap nuts, acorn nuts have a rounded, domed top, but they are typically used in applications where a more decorative finish is desired.
↪ Wing Nuts: These nuts have "wings" or projections that allow for hand tightening, making them convenient for applications where frequent adjustments are needed.
↪ Square Nuts: Square nuts have a square shape and are often used in conjunction with square-headed bolts or threaded rods, preventing rotation during tightening.
↪ Lock Nuts: Lock nuts have special features to prevent loosening due to vibrations or torque. Examples include nylon-insert lock nuts, prevailing torque lock nuts (such as prevailing torque hex nuts or flange nuts), and distorted thread lock nuts.
Metric Sizes:
↪ M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20, M24, M30, M36, etc.
↪ These sizes correspond to the diameter of the threaded portion of the bolt or screw with which the nut is intended to be used.
Imperial (Inch) Sizes:
↪ 6-32, 8-32, 10-24, 1/4"-20, 5/16"-18, 3/8"-16, 7/16"-14, 1/2"-13, 5/8"-11, 3/4"-10, etc.
↪ These sizes are denoted by the diameter of the bolt or screw followed by the number of threads per inch.
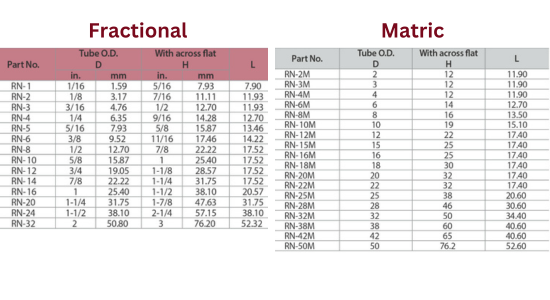
Fractional and Matric
Function
↪ The primary function of a nut is to apply compressive force to the joint, thereby holding the connected parts firmly in place.↪ Nuts are fasteners that secure objects together by creating a threaded connection. They are typically used in conjunction with bolts, screws, or threaded rods.
Materials
↪ Nuts are manufactured from a variety of materials, including steel, stainless steel, brass, aluminium, nylon, and plastic.↪ The choice of material depends on factors such as the application environment, required strength, corrosion resistance, and cost considerations.
Sizes and Standards
↪ Nuts are available in a wide range of sizes and thread pitches to accommodate different bolt or screw sizes.↪ They are manufactured according to various standards, such as metric (e.g., ISO, DIN) or imperial (e.g., ANSI/ASME), ensuring compatibility and interchangeability with other components.
Applications
↪ Nuts are used across numerous industries and applications, including automotive, construction, machinery, aerospace, electronics, and furniture assembly.↪They play a critical role in securing structural components, fastening machine parts, assembling equipment, and maintaining the integrity of mechanical systems.
